Explain Why Pulse Pressure Is Different From Pulse Rate
A high pulse pressure or wide pulse pressure is above 60 mmHg. Difference between Systolic el diastolic pressure Why is this measurement important.

Cv Physiology Arterial And Aortic Pulse Pressure
View the full answer.

. Sitting and laying down decreased heart rate by 15 bpm and 95 bpm respectively. Pulse pressure is also independently associated with an increased risk of developing atrial fibrillation. The relative amount of muscular contraction present in these postures has no appreciable effect.
For example if the resting blood pressure is 12080 millimeters of mercury mm Hg the pulse. Heart rate or pulse is the number of times the heart beats per minute BPM. Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure and the pulse rate is the pressure surges per minute.
Childs pose is not the most effective of the tested poses at returning heart rate to baseline. It causes a change in blood pressure and pulse rate in the main arteries. Pulse pressure systolic pressure - diastolic pressure.
Adults 18 years and older. Explain why pulse pressure is different from pulse rate. Calculating blood pressure requires a sphygmomanometer blood pressure machine or monitor.
Thereforethe pulse rate is essentially your heart rate. Venous pressures are so much lower than arterial pressures because the veins are further removed from the pumping action of the heart. The bottom number is the amount of pressure in the arteries between beats diastolic pressure.
A heart rate is the number of times your heart beats in the span of a minute. Since the pulse is produced by the rise in pressure from dia-stolic to systolic levels the difference between these two pressures is known as the pulse pressure. Hemorrhage increased blood viscosity 5.
According to Biology Online homeostasis uses a negative and positive feedback system to keep the human body running efficiently. Question No23 Answer. What effect do the following have on blood pressure.
The blood pressure consists of the pressure the blood exudes on the walls of the arteries as it flows through the body. Previous question Next question. Children 6 to 15 years.
How do venous pressures compare to arterial pressures. The portion of the brain stem that controls the heart rate is the medulla. Pulse rate can be counted manually or by using a pulseoxymeter while the blood pressure is taken using the sphygmomanometer.
As pulse pressure rises risk of diabetes chronic kidney. The sitting-lying difference is due to hydrostatic influence acting. Knowing the heart rate alone cannot determine what the bodys blood pressure reading is.
It may be defined as the difference between systolic and diastolic. The medulla transmits chemical messages and nerve impulses through the medulla pyramids. Indicate increase by t and decrease by 1.
The heart rate is the measured value obtained per minute when listening to the sounds the heart produces. Heart rate measures the contractions of a heart ie. In pulse rate only one measurement is taken while in blood pressure two measurements are taken as systolic and diastolic pressures.
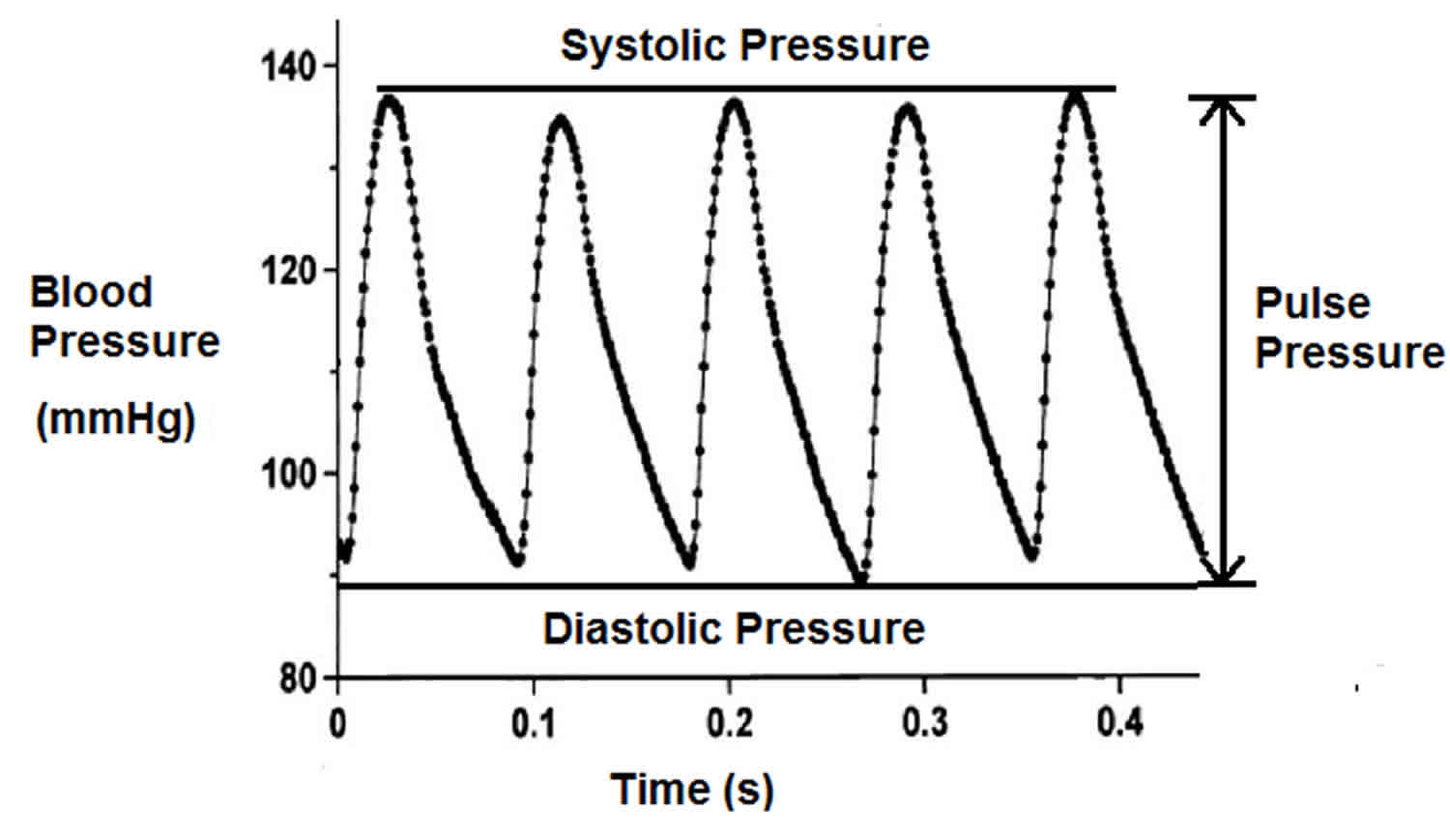
Increased pulse rate 29. A study done by Mitchell et al. A person with a blood pressure of 12080 systolicdiastolic would therefore have a pulse pressure of 40 mmHg.
60 to 100 BPM. However according to the new guidelines issued by the AHA the goal BP for all adults is now less than 13080 mm Hg. Furthermore a heartbeat pushes the blood throughout a human body.
Ill inform you if blood pressure and heart rate moves up and down together or if one. Showed that patients with a pulse pressure of 40 mmHg or less developed atrial fibrillation at a rate of 56 whereas patients with a pulse pressure greater than 61 mmHg developed atrial fibrillation at a rate of 233. Increased cardiac output 46.
The pulse rate is the measured value per minute when palpating the arterial vessels through. On the other hand the pulse rate calculates the frequency in which palpable blood pressure surges in ones body. This article will dive into the blood pressure and heart rate relationship.
In which position sitting reclining or standing is the blood. A pulse rate is the number of times your arteries create a noticeable pulse due to increase in blood pressure as a result of your heart contracting. The slowed pulse-rate in the horizontal posture as compared with sitting and the quicker rate in standing as compared with sitting depend on wholly different mechanisms and may vary independently.
Variations in these two entities give clues to different disease conditions. However heart rate and pulse rate are technically different because a heart rate measures the rate of contractions heart beats of the heart whereas a pulse rate measures the rate of palpable blood pressure increases throughout the body. Normal resting heart rates are as follows.
The blood pressure and pulse are two very different measurements but they have the heart as their common denominator. Increased diameter of the arterioles 4. 70 to 100 BPM.
In healthy individuals this means the heart rate is often synchronized with the pulse. While its common for pulse pressure to increase with advancing age pulse pressure above 60 mmHg could be a warning sign for heart disease heart attack stroke and other serious conditions especially in older adults. The two forces at work during this process--known commonly as the readings or as systolic and diastolic.
In comparing baseline heart rate to after-pose heart rate Childs pose and standing increased heart rate by 95 bpm and 10 bpm respectively. The top number is the maximum pressure the heart exerts while beating systolic pressure. Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure and the pulse rate is the pressure surges per minute.
The top number systolic minus the bottom number diastolic is the pulse pressure.
Pulse Pressure Definition Wide Pulse Pressure Narrow Pulse Pressure Causes

No comments for "Explain Why Pulse Pressure Is Different From Pulse Rate"
Post a Comment