Chromosomal Replication Produces Two Identical Sister Chromatids
This replication produces two identical copies called sister chromatids that are held together at the centromere by cohesin proteins. In humans cells containing two copies of each of the 23 chromosomes are called _____.
Solved Drag The Terms On The Left To Correctly Complete Chegg Com
During S phase eukaryotic chromosomes are replicated to produce a pair of identical sister chromatids that.

. During mitosis microtubules attach to chromosomes at the centrosomes 4. The centrosomes which are the structures that organize the microtubules of the meiotic spindle also replicate. After chromosomes condense the centromeres is the region where the identical DNA molecules are most tightly attached to each other.
After chromosomes condense the is the region where the identical DNA molecules are most tightly attached to each other. The two identical chromosomes that result from DNA replication are referred to as sister chromatids. The main difference between sister chromatids and non-sister chromatid is that sister chromatid discusses the identical copies form by the DNA replication of a chromosome when both copies join together by a common centromere whereas non-sister chromatid refers to either one of the two chromatids of pair homologous chromosomes.
Sister chromatids result from DNA replication in the S phase and are identical to each other. One copy is from the mother and one is from the father. Sister chromatids are two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome that are connected by a centromereChromosome replication takes place during interphase of the cell cycle.
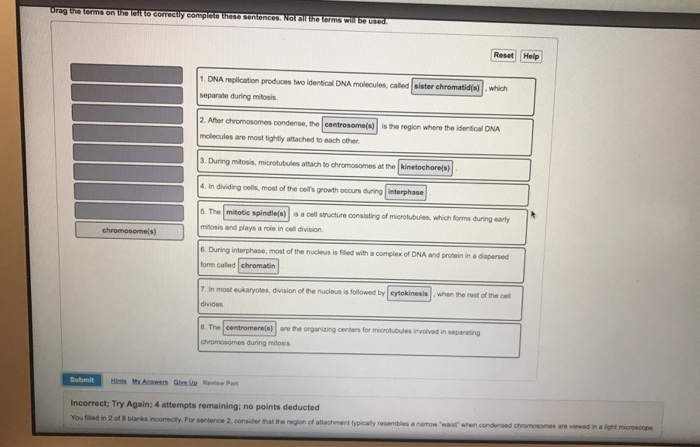
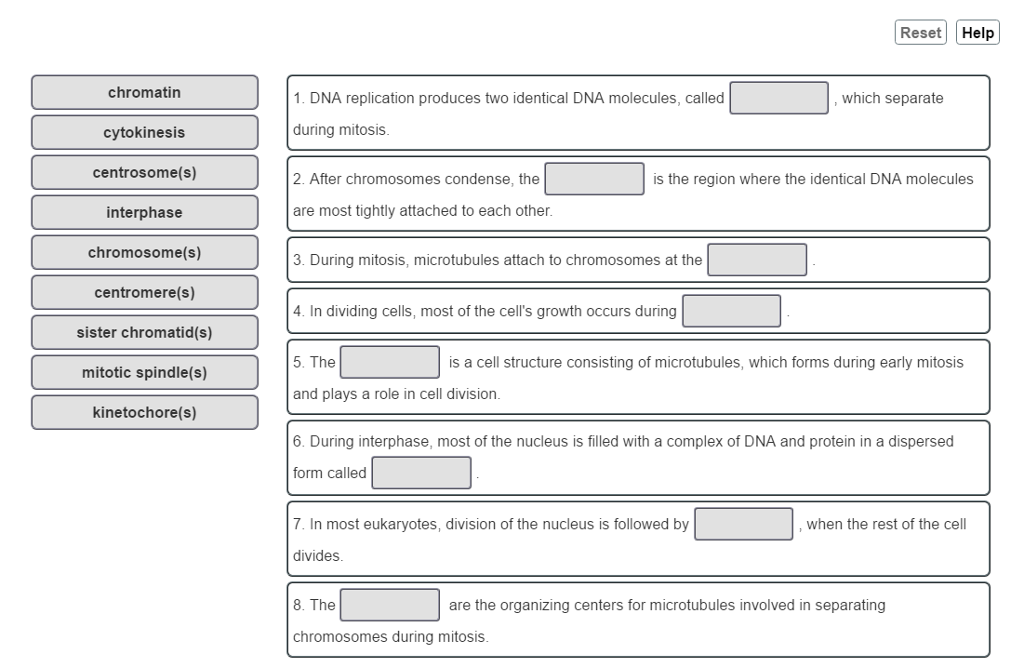
The term homologous chromosomes refers to replications of the same chromosome is another name for sister chromatids must be haploid means a pair of chromosomes of the same kind such as sex chromosomes The term not related to mitosis is gametes chromosomes DNA replication somatic cells At the _____ checkpoint cell growth is. DNA replication produces two identical DNA molecules called sister chromatids which separate during mitosis. When fully condensed replicated chromosomes appear as thick X-shaped structures that are readily.
These two copies are _____ to each other. DNA replication produces two identical DNA molecules called _____ which separate during mitosis. Sister chromatids are two identical copies of the same chromosome formed by DNA replication attached to each other by a structure called the centromere.
During cell division they are separated from each other and each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. A chromatid is one of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome. Similarly you may ask why does each chromosome.
After chromosomes condense the centromeres is the region where the identical DNA molecules are most tightly attached to each other. Because each chromosome was duplicated during S phase it now consists of two identical copies called sister chromatids that are attached at a. In dividing cells most of the cells growth occurs during.
Differences between Sister Chromatids and Non-Sister Homologous Chromatids. Chromosomes undergo additional compaction at the beginning of mitosis. During cell division the chromosomes first replicate so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
During cell division they are separated from each other and each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. Sister chromatids are held together by proteins at a region of the chromosome called the centromere. DNA replication produces two identical DNA molecules called which separate during mitosis.
The S phase is next during which the DNA of the chromosomes is replicated. In dividing cells most of the. Click to see full answer.
In the process of mitotic cell division a cell divides to produce two new cells the daughter cells that are genetically identical to the original cell. During mitosis microtubules attach to chromosomes at the. After the S phase and DNA replication each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids.
Sister chromatids After chromosomes condense the _______ is the region where the identical DNA molecules are most tightly attached to each other. During mitosis microtubules attach to chromosomes at the kinetochores. DNA replication produces two identical DNA molecules called sister chromatids which separate during mitosis.
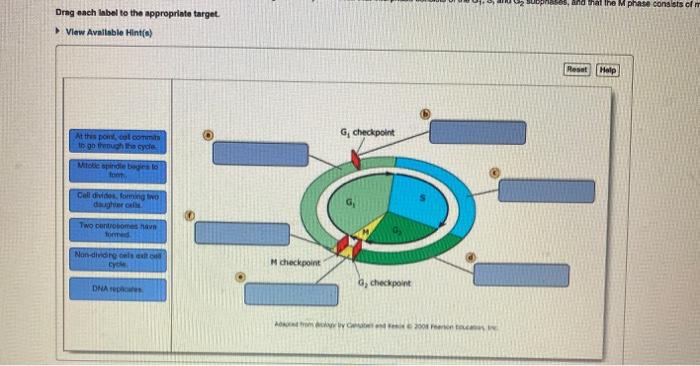
Chromosomal replication produces two identical sister chromatids. Skin and breast cancer cells that are undergoing uncontrolled cell division have been treated with chemicals that prevent them from proliferating by causing the cells to arrest before the DNA starts to replicate. Sister chromatids are two identical copies of the same chromosome formed by DNA replication attached to each other by a structure called the centromere.
DNA is synthesized during the S phase or synthesis phase of interphase to ensure that each cell ends up with the correct number of chromosomes after cell. Following DNA replication the chromosome consists of two identical structures called sister chromatids which are joined at the centromere.

Solved Dna Replication Produces Two Identical Dna Molecules Chegg Com
Solved Chromatin Cytokinesis Centrosome S Interphase Chegg Com
Solved Drag The Terms On The Left To Correctly Complete Chegg Com
No comments for "Chromosomal Replication Produces Two Identical Sister Chromatids"
Post a Comment